In modern manufacturing, precision, durability, and efficiency are essential for producing high-quality components. One of the key methods for achieving these goals is shell mold casting, a process widely used across industries for producing complex metal parts with excellent surface finishes. The products of this process, known as Shell Mold Casting Parts, are integral to industries ranging from automotive to aerospace due to their precision and reliability.
Investing in quality Shell Mold Casting Parts ensures that manufacturers can meet stringent design and performance requirements. Unlike traditional casting methods, shell mold casting uses a fine sand and resin mixture to create thin, hard molds that enable intricate details and superior dimensional accuracy. This makes it ideal for producing parts that require tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
The Manufacturing Process of Shell Mold Casting Parts
1. Creating the Pattern
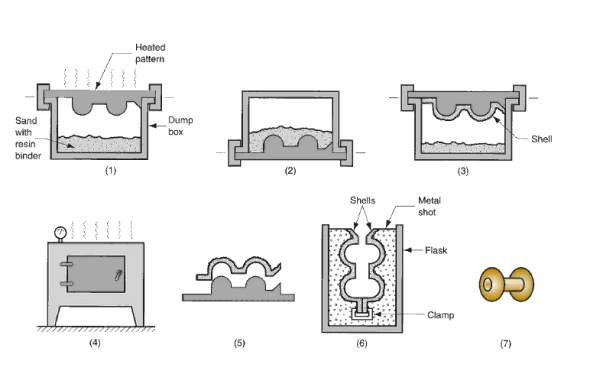
The process begins with the creation of a pattern, typically made from metal, plastic, or wood. This pattern is an exact replica of the part to be cast and serves as the foundation for building the mold. The precision of the pattern is crucial, as it directly impacts the accuracy of the final product.
2. Applying the Shell
In shell mold casting, a mixture of fine sand and thermosetting resin is applied to the heated pattern. The heat causes the resin to partially cure, forming a thin shell layer. This process is repeated multiple times to achieve the desired mold thickness, ensuring strength and durability during the casting process.
3. Hardening and Baking
Once the shell reaches the required thickness, it is carefully removed from the pattern and baked to fully cure the resin. This hardening process enhances the mold’s structural integrity, enabling it to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of molten metal during casting.
4. Assembling the Mold
The individual shell halves are then assembled and joined to form the complete mold. Any gating and venting systems required for metal flow and air escape are integrated at this stage. Proper assembly ensures uniform metal flow and minimizes defects in the final casting.
5. Pouring and Cooling
Molten metal is poured into the assembled shell mold, filling the cavity created by the original pattern. The metal solidifies quickly due to the thin shell walls, reducing the likelihood of shrinkage and improving dimensional accuracy. After cooling, the shell mold is broken away to reveal the finished casting.
6. Finishing and Inspection
The cast parts undergo finishing processes such as grinding, machining, or polishing to achieve the desired surface quality and dimensional tolerances. Each part is carefully inspected to ensure it meets industry standards and functional requirements.
Applications of Shell Mold Casting Parts
Shell mold casting parts are widely used across multiple industries due to their precision, strength, and smooth surface finish.
Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, these parts are used for engine components, transmission housings, and suspension parts. Their dimensional accuracy and durability make them suitable for high-performance and safety-critical applications.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector benefits from shell mold casting for components like turbine blades, structural brackets, and other precision parts. The process allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances, essential for maintaining safety and performance in aerospace applications.
Industrial Machinery
Shell mold casting parts are used in industrial machinery for gears, pumps, and other equipment requiring strong, wear-resistant components. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress ensures long-term reliability.
Consumer Products
Even in consumer products, shell mold castings provide durable, aesthetically appealing components for appliances, tools, and other high-end items.
Advantages of Shell Mold Casting
- High Precision: The thin mold walls allow for fine details and tight tolerances.
- Superior Surface Finish: Parts typically require minimal post-processing.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Efficiency: Faster cooling and solidification reduce production time and defects.
Conclusion
Shell Mold Casting Parts are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering precision, durability, and versatility for a variety of industrial applications. By combining advanced mold-making techniques with high-quality materials, manufacturers can produce components that meet demanding specifications while maintaining cost efficiency.
For industries requiring reliable, high-performance parts with intricate designs and smooth finishes, shell mold casting remains an essential and highly effective solution.