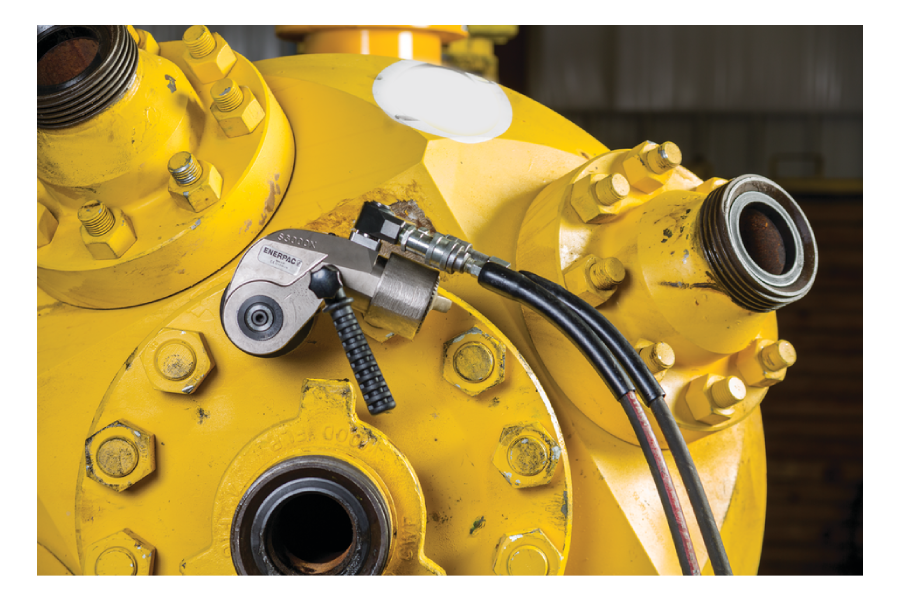
In modern industrial operations, precision fastening is not a minor detail—it is a foundation of safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability. Heavy machinery, pressure systems, structural assemblies, and rotating equipment all depend on fasteners that are tightened to exact specifications. Even a small deviation in torque can lead to leaks, vibration issues, premature wear, or catastrophic failure. This is why industries handling high loads and critical joints demand advanced torque technology rather than conventional hand tools.
A hydraulic torque wrench is engineered to meet these high-stakes requirements by delivering accurate, controlled torque for large-scale bolting applications. Designed for strength, consistency, and operator safety, this tool has become a cornerstone in sectors where precision and repeatability are essential.
The Science Behind Hydraulic Torque Application
Hydraulic torque technology works by converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force. A pump generates pressurized fluid, which flows through reinforced hoses into the wrench body. Inside the tool, this pressure drives a piston mechanism that rotates the drive, applying torque to the fastener in a smooth and controlled manner.
This controlled motion is one of the biggest advantages of hydraulic systems. Unlike impact-based tools that rely on sudden force, hydraulic torque delivers steady and measurable output. This minimizes stress on bolts and joints while ensuring that torque values are achieved accurately and consistently.
Why Precision Matters in Industrial Bolting
In heavy-duty environments, bolts are not just holding parts together—they are maintaining pressure boundaries, load distribution, and structural balance. Uneven or incorrect torque can cause several issues, including:
- Flange leaks in pipelines and pressure vessels
- Fatigue cracks due to uneven load distribution
- Increased vibration in rotating machinery
- Costly downtime and safety hazards
Hydraulic torque tools address these risks by ensuring uniform torque across all fasteners in an assembly, which directly improves joint integrity and operational lifespan.
Key Components of a Hydraulic Torque System
A complete hydraulic torque setup consists of multiple components working in harmony:
Hydraulic Pump
The pump is the power source of the system. It controls pressure output, which directly correlates to applied torque. Pumps may be electric, pneumatic, manual, or battery-operated depending on site conditions.
Torque Wrench Unit
This is the main working tool that applies torque to the fastener. It is designed to withstand high loads and repeated use in harsh environments.
High-Pressure Hoses
These hoses transfer hydraulic fluid from the pump to the wrench. They are reinforced to handle extreme pressures safely.
Reaction Arm or Cassette
The reaction mechanism absorbs counterforce during operation, preventing tool rotation and ensuring stable, safe use.
Each component is manufactured to strict tolerances to ensure performance reliability under demanding conditions.
Types of Hydraulic Torque Wrenches and Their Uses
Different applications require different wrench configurations. The most common types include:
Square Drive Hydraulic Torque Wrenches
These are versatile and widely used. They accept interchangeable sockets, making them suitable for maintenance and repair tasks involving various bolt sizes.
Low-Profile Hydraulic Torque Wrenches
Designed for confined or restricted spaces, these tools are commonly used in flange connections where clearance is limited.
Custom and Specialized Solutions
Some industries require customized torque tools for extreme environments, such as subsea operations, hazardous zones, or high-temperature applications.
Choosing the right type ensures efficiency, safety, and long-term performance.
Industries That Rely on Hydraulic Torque Technology
Hydraulic torque systems are trusted across a wide range of industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: Pipelines, refineries, offshore platforms, and pressure vessels
- Power Generation: Turbines, generators, boilers, and structural assemblies
- Wind Energy: Tower flanges, nacelles, and blade connections
- Heavy Construction: Bridges, cranes, and steel frameworks
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Engine mounts, deck equipment, and propulsion systems
In each case, accurate torque application is critical to preventing failure and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Advantages Over Traditional Torque Methods
Hydraulic torque tools offer clear benefits compared to manual or impact-based alternatives:
- High Accuracy: Precise control over torque values
- Repeatability: Consistent results across multiple fasteners
- Improved Safety: Reduced operator strain and controlled force application
- Time Efficiency: Faster tightening cycles for large bolting projects
- Durability: Built to perform reliably in harsh industrial conditions
These advantages translate into reduced maintenance costs, fewer failures, and improved overall productivity.
Safety Practices for Optimal Performance
While hydraulic torque tools enhance safety, proper operation remains essential. Best practices include:
- Verifying torque specifications before starting
- Inspecting hoses, seals, and fittings regularly
- Ensuring the reaction arm is securely positioned
- Using calibrated pumps and gauges
- Following manufacturer-recommended procedures
Operator training plays a major role in maximizing both safety and tool lifespan.
Maintenance, Calibration, and Reliability
Regular maintenance is crucial for preserving accuracy and performance. Hydraulic fluid levels should be checked, seals inspected, and worn components replaced as needed. Calibration ensures that torque output remains within specified tolerances, which is especially important in regulated industries such as energy and petrochemicals.
Preventive maintenance not only extends equipment life but also protects critical infrastructure by ensuring fasteners are tightened correctly every time.
How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Torque Solution
Selecting the right system involves evaluating several factors:
- Required torque range
- Space limitations at the job site
- Frequency of use
- Environmental conditions
- Available power sources
Working with a trusted supplier that offers technical support, calibration services, and after-sales assistance can significantly improve long-term value.
The Future of Hydraulic Torque Technology
As industrial standards evolve, hydraulic torque solutions continue to advance. Innovations such as digital pressure gauges, torque data logging, lighter materials, and battery-powered pumps are making these tools more efficient and user-friendly. These developments support higher safety standards, improved quality control, and greater operational transparency.
Final Thoughts
In high-risk, high-load environments, precision fastening is not optional—it is essential. Hydraulic torque technology provides the accuracy, consistency, and reliability required to secure critical joints across a wide range of industries. By understanding how these tools work and applying best practices, organizations can reduce downtime, enhance safety, and ensure long-term operational success.