Press machines are essential equipment in manufacturing, used for operations such as stamping, punching, bending, and forming metal components. The efficiency, precision, and safety of a press machine depend on the proper design and functioning of its key components. Understanding these components helps manufacturers, operators, and maintenance personnel optimize performance and ensure long-term reliability.
A reliable Press Machine is composed of multiple interdependent components that work together to perform high-precision metal forming tasks. Each component has a specific function, and any failure or misalignment can compromise the machine’s performance and safety. By understanding the role and operation of each part, users can maintain the machine effectively, reduce downtime, and enhance overall productivity.
Frame
The frame is the backbone of a press machine, providing structural support for all other components. It must be rigid and durable to withstand high forces and repeated stress during operation. Frames are usually made of cast iron or welded steel and are designed to minimize vibrations and maintain alignment between the ram and bed. The type of frame—C-frame, H-frame, or straight-side—affects the accessibility, stability, and capacity of the machine. A strong frame ensures consistent performance and reduces wear on other components.
Ram or Slide
The ram, also known as the slide, is the moving part of a press machine that applies force to the workpiece. It moves vertically under mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic action to shape, punch, or bend the material. Precision in the movement of the ram is critical, as any misalignment can lead to uneven pressure, material deformation, or die damage. Modern press machines often include servo-controlled rams for enhanced accuracy and customizable motion profiles.
Bed or Table
The bed, sometimes referred to as the machine table, provides a stable surface for placing the die and the workpiece. It is usually fixed and constructed from high-strength materials to endure repeated force application. Proper alignment between the bed and the ram is essential for accurate forming operations. Many beds feature T-slots or clamping points to securely hold dies and tooling, ensuring precision and repeatability in production.
Die and Tooling
Dies and tooling are the actual components that shape or cut the material in a press machine. They are installed between the ram and the bed and are designed according to the desired part geometry. Dies may be single-action, double-action, progressive, or compound, depending on the complexity of the operation. High-quality dies reduce material waste, maintain dimensional accuracy, and extend tool life. Regular inspection and maintenance of dies are essential for consistent machine performance.
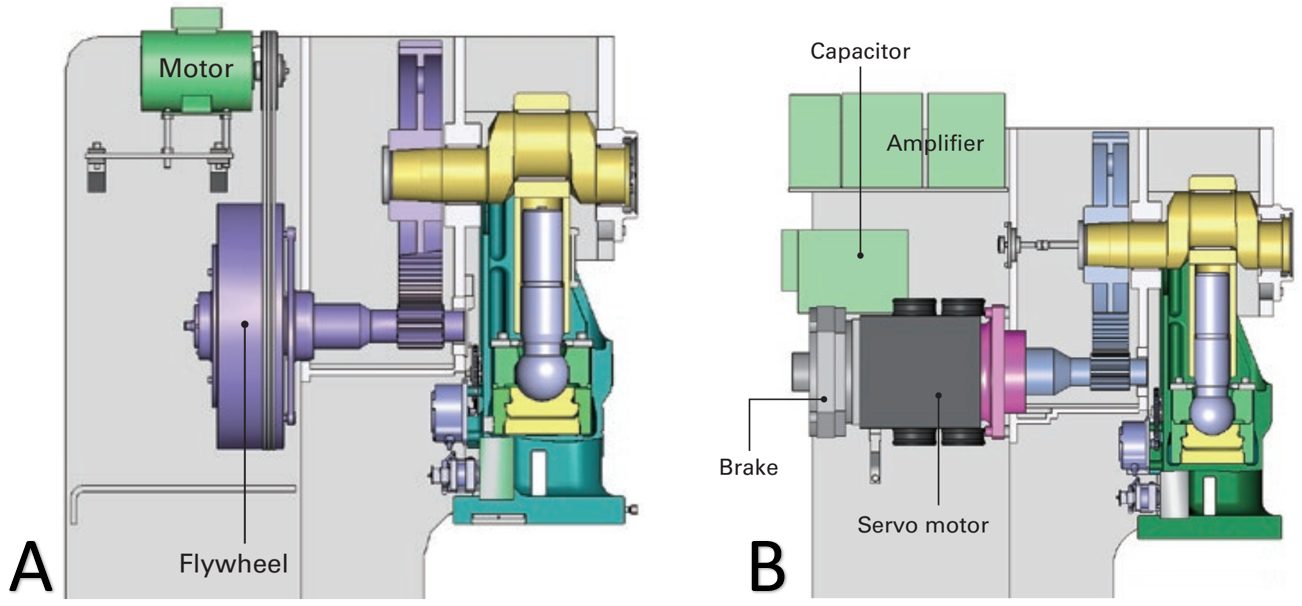
Flywheel and Drive System
The flywheel stores mechanical energy and transfers it to the ram through a drive system, which may include gears, clutches, or belts. In mechanical presses, the flywheel provides rapid and powerful movement, allowing for high-speed operations. Hydraulic or servo drives offer more control over stroke, force, and speed, making them suitable for heavy-duty or precise operations. The drive system must be properly maintained to ensure smooth energy transfer and prevent unexpected downtime.
Safety Components
Modern press machines incorporate multiple safety components to protect operators and prevent accidents. Common safety features include emergency stop buttons, light curtains, interlocks, two-hand control systems, and pressure-sensitive mats. These components detect unsafe conditions and immediately halt machine operation. Regular testing and calibration of safety systems are crucial to maintaining a secure working environment.
Lubrication and Cooling Systems
Lubrication systems reduce friction between moving parts, extending component life and ensuring smooth operation. Proper lubrication prevents overheating, wear, and premature failure. Some press machines also include cooling systems, particularly in hydraulic models, to maintain optimal fluid temperature and prevent thermal expansion that can affect accuracy and efficiency.
Control Panel
The control panel is the interface through which the operator manages machine functions, including start/stop, speed adjustment, stroke length, and safety system monitoring. Advanced press machines include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or touchscreen interfaces that allow for automation, data logging, and real-time monitoring. The control system ensures consistent operation, reduces operator errors, and supports production efficiency.
Conclusion
A press machine is a complex assembly of interdependent components, each playing a vital role in ensuring precision, efficiency, and safety. Key components such as the frame, ram, bed, die, flywheel, drive system, safety mechanisms, lubrication systems, and control panels work together to perform high-precision metal forming tasks. Understanding the function and maintenance requirements of these components allows operators and manufacturers to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and extend machine life. A reliable Press Machine integrates these components efficiently, providing durable, safe, and precise equipment for modern manufacturing environments.